2. Classification of migrations: waves of population characteristics
 Click image to enlarge
Click image to enlarge
Source: Chart taken from G. Calafiore, Migrazioni, in Le parole chiave della geografia, a cura di G. De Vecchis e C. Palagiano, Carocci, Roma 2003, p. 192; a synopsis by Silvana Bianchi (Verona University and Ca’ Foscari University ).
Questions
Description and Analysis
Migratory movements are different in time and space and still, in order to be understood and and compared, some fundamental classification guidelines need to be picked out.
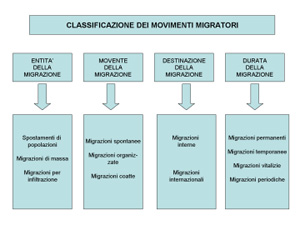
Geography scholars have provided different classification (often set on the basis of specific key-factors); the one we are going to consider here has been recently pointed out by Human Geography scholar Giovanni Calafiore.
- With an extent ranking it is possible to quantify the numeric size. (only a few past eras and not always trustworthy for the present nor for the past illegal migrations)
The most important migrations are movements of population which involve huge displacements of individuals and produce long-lasting consequences. Mass migrations involve a lesser number of people whose migration is a consequence of traumatic events. Migrations through infiltration , on the other hand , involve small-sized displacements of individuals or restricted groups, that are moving without causing any particular changing. - Motive ranking: it analyses the moving basic reasons which are often a few. It is also meant to determine the main one. 2722473
Spontaneous migrations come from single decisions of individuals. Arranged migration are promoted and supported by an authority towards open spaces destinations destined for business settlement. Forced migrations become mandatory because of dramatic happenings which require a transfer. - Destination ranking: it picks out arrival areas and domestic movements and those heading to foreign countries.
Domestic migrations are those remaining within the state boundaries and are the most difficult to quantify. ( that is because many people keep their official address in their home town). International migrations are those heading to foreign countries are, theoretically, under control more than any others. However they include, in fact, a significant illegal component which is hard to quantify. - Length ranking: it divides migrations on the basis of their time duration.
Permanent migrations involve those who permanently settle down in some other place (with positive effects for the hosting country which can therefore benefit from their workforce). Temporary migrations are made up by phenomena that are limited in time and refer to working age males (this has a positive influence for the exporting country thanks to the emigrants remittances and thanks to cultural and professional skills they ___) Life-long migrations are those where a migrant returns home only when he is elderly (and most benefits go to the hosting country). Periodic migrations are connected to particular cultural o economic cycles. Nowadays they are faltering except for the seasonal tourism which is still particularly gainful.
Links
- http://www.psicologiaintransito.it/luttomigratorio.html = a closer look to the topic “migratory mourning” with refers to the family ties loss for those who leave their home country (for cross-disciplinary activities )taken from the website http://www.psicologiaintransito.it/index.html by Stefania Mezzullo.
- http://www.museonazionaleemigrazione.it/museo.php?id=3 = MEI home page, National Italian Migration Museum. It provide material on Italians migration experiences.
- http://www.cmmigrants.org/goree = Word Migrants Convention website.
- http://www.comunicazione.uniroma1.it/materiali/15.28.52_Migrazioni%20globali.doc = an excerpt about “Anthropology and global migrations ” taken from La Sapienza Rome University website




Presentation
Migrations are a quite complex phenomenon too difficult to enclose in a single scheme. To understand these, anyway, historians, geographics and anthropologists have been trying to classify them in order to emphasize some specific and basic features which are fundamental to understand them. Such a scheme is to pick out four referential sectors for the amount of people on the move, causes, destinations and duration.