2. Maps of European internal borders in the 20th century
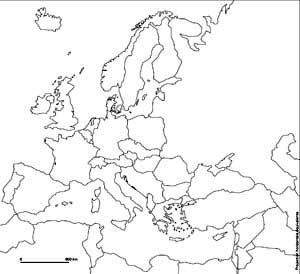
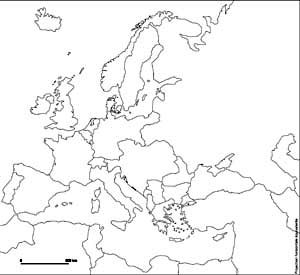
Map A. 1945-1949
Source: Atelier de cartographie de Sciences Po, 2007, http://www.sciences-po.fr/cartographie.
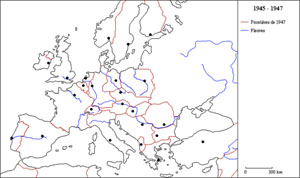
Map B. 1993-1994
Source: Atelier de cartographie de Sciences Po, 2007, http://www.sciences-po.fr/cartographie.
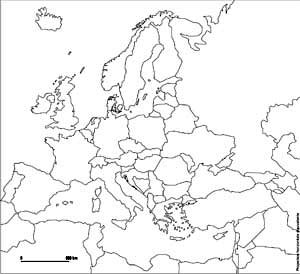
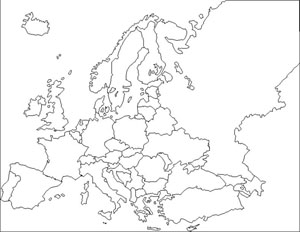
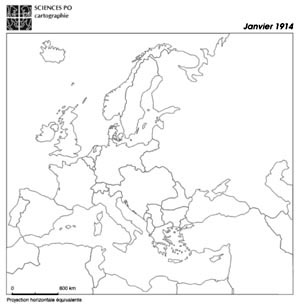
Map C. 1914
Source: Atelier de cartographie de Sciences Po, 2007, http://www.sciences-po.fr/cartographie.
Map D. 1920-1938
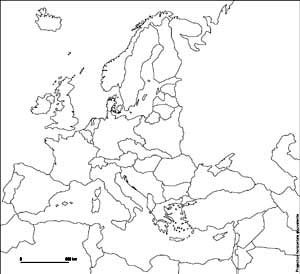 Click image to enlarge
Click image to enlarge
Source: Atelier de cartographie de Sciences Po, 2007, http://www.sciences-po.fr/cartographie.
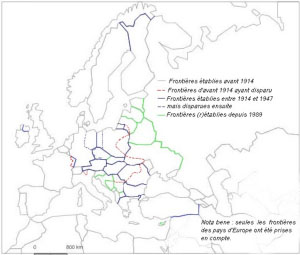
Map E available for transferring all the borders to the base map of 2010
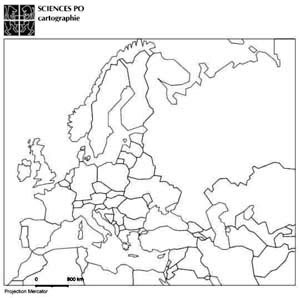 Click image to enlarge
Click image to enlarge
Source: Atelier de cartographie de Sciences Po, 2007, http://www.sciences-po.fr/cartographie.
Questions
Suggestion of Activities
- Question 1: Examination and comparison of national borders in Europe at different times. The students must recognize and justify their choice of the map of Europe in the early twentieth century (1914), the map depicting the period between the wars (1919-1938), the one after the Second World War (1945-1949) and the map of Europe in the late twentieth century (1993). The analysis of provided justifications will point out traces of specific tendencies (countries are becoming increasingly large, borders tend to disappear, etc.) and stress the significanceof knowledge about the former boundaries. We particularly emphasize the importance of the treaties signed at the end of the First World War.
- Question 2: This analytical point of view on historical maps will help to structure the different stages of regionalization of the European space. It will primarily show that most of European borders have been created rather recently, which is conspicuous even in Eastern Europe. We particularly want to emphasize that each territorial change has accompanied a frontier settlement after a military conflict to show that borders also illustrate changing balances of powers.
Exercise corrected
Of course, Central Europe is characterized by a lot of border changes. There has been always a tendency to push the Russian borders to the east. The borders between Germany and Poland, which have been the ones most frequently changed, are within the European Union today.